N N Dimethylglycine Hcl Dmg
- N N-dimethylglycine Hcl (dmg)
- N N Dimethylglycine Dmg
- N N-dimethylglycine For Cats
- N Dimethylglycine Dmg Side Effects

Mar 04, 2015 Dimethylglycine, also known as DMG, is an amino acid found in small amounts throughout the body. Today, dimethylglycine is used primarily in nutritional supplements and medicine. Find out everything you need to know about Dimethylglycine today in our DMG review! What is Dimethylglycine? Dimethylglycine is a derivative of an amino acid called. Dimethylglycine is a highly unusual supplement, in that it is extremely popular despite the fact that all of its touted effects have largely been refuted by clinical and laboratory testing.
Sep 17, 2019 Dimethylglycine might be safe to use short-term, up to 28 days. The safety of long-term use is unknown. Special Precautions & Warnings: Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Not enough is known about the use of dimethylglycine during pregnancy and breast-feeding.
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| Other names N,N-Dimethylglycine | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| 3DMet | |
| 1700261 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.971 |
| EC Number |
|
| 82215 | |
| KEGG |
|
| MeSH | dimethylglycine |
| RTECS number | |
CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H9NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 103.121 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Density | 1.069 g/mL |
| Melting point | 178 to 182 °C (352 to 360 °F; 451 to 455 K) |
| Boiling point | 175.2 °C (347.4 °F; 448.3 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| >650 mg kg−1(oral, rat) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids | |
| Dimethylacetamide | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| verify (what is ?) | |
| Infobox references | |
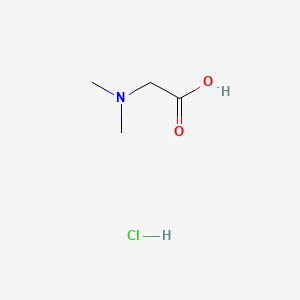
Dimethylglycine (DMG) is a derivative of the amino acidglycine with the structural formula (CH3)2NCH2COOH. It can be found in beans and liver. It can be formed from trimethylglycine upon the loss of one of its methyl groups. It is also a byproduct of the metabolism of choline. El capitan download.
When DMG was first discovered, it was referred to as Vitamin B16, but, unlike true B vitamins, deficiency of DMG in the diet does not lead to any ill-effects and it is synthesized by the human body in the citric acid (or Krebs) cycle meaning it does not meet the definition of a vitamin.
Uses[edit]
N N-dimethylglycine Hcl (dmg)
Dimethylglycine has been suggested for use as an athletic performance enhancer, immunostimulant, and a treatment for autism, epilepsy, or mitochondrial disease.[2] There is no evidence that dimethylglycine is effective for treating mitochondrial disease.[3] Published studies on the subject have shown little to no difference between DMG treatment and placebo in autism spectrum disorders.[4][5]
Biological activity[edit]
N N Dimethylglycine Dmg
Dimethylglycine has been found to act as an agonist of the glycine site of the NMDA receptor.[6]
Preparation[edit]
This compound is commercially available as the free form amino acid, and as the hydrochloride salt [2491-06-7 ]. DMG may be prepared by the alkylation of glycine via the Eschweiler–Clarke reaction. In this reaction, glycine is treated with aqueous formaldehyde in formic acid that serves as both solvent and reductant. Hydrochloric acid is added thereafter to give the hydrochloride salt. The free amino acid may have been obtained by neutralization of the acid salt, which has been performed with silver oxide.[7]
- H2NCH2COOH + 2 CH2O + 2 HCOOH → (CH3)2NCH2COOH + 2 CO2 + 2 H2O
N N-dimethylglycine For Cats
References[edit]
N Dimethylglycine Dmg Side Effects
- ^'dimethylglycine - Compound Summary'. PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ^'Dimethylglycine'. About Herbs, Botanicals & Other Products. Memorial Sloan–Kettering Cancer Center. December 8, 2009.
- ^Pfeffer, Gerald; Majamaa, Kari; Turnbull, Douglass M.; Thorburn, David; Chinnery, Patrick F. (2012-04-18). 'Treatment for mitochondrial disorders'. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD004426. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004426.pub3. ISSN1469-493X. PMID22513923.
- ^Bolman WM, Richmond JA (June 1999). 'A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover pilot trial of low-dose dimethylglycine in patients with autistic disorder'. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 29 (3): 191–4. doi:10.1023/A:1023023820671. PMID10425581.
- ^Kern JK, Miller VS, Cauller PL, Kendall PR, Mehta PJ, Dodd M (March 2001). 'Effectiveness of N,N-dimethylglycine in autism and pervasive developmental disorder'. Journal of Child Neurology. 16 (3): 169–73. doi:10.1177/088307380101600303. PMID11305684.
- ^Lin, Jen-Cheng; Chan, Ming-Huan; Lee, Mei-Yi; Chen, Yi-Chyan; Chen, Hwei-Hsien (2016). 'N,N-dimethylglycine differentially modulates psychotomimetic and antidepressant-like effects of ketamine in mice'. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 71: 7–13. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.06.002. ISSN0278-5846. PMID27296677.
- ^Clarke, H. T.; Gillespie, H. B.; Weisshaus, S. Z. (1933). 'The Action of Formaldehyde on Amines and Amino Acids'. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 55 (11): 4571. doi:10.1021/ja01338a041.